An option is a contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price on or before a certain date. An option, just like a stock or bond, is a security. It is also a binding contract with strictly defined terms and properties.
Still confused? The idea behind an option is present in many everyday situations. Say, for example, that you discover a house that you'd love to purchase. Unfortunately, you won't have the cash to buy it for another three months. You talk to the owner and negotiate a deal that gives you an option to buy the house in three months for a price of $200,000. The owner agrees, but for this option, you pay a price of $3,000.
Now, consider two theoretical situations that might arise:
1. It's discovered that the house is actually the true birthplace of Elvis! As a result, the market value of the house skyrockets to $1 million. Because the owner sold you the option, he is obligated to sell you the house for $200,000. In the end, you stand to make a profit of $797,000 ($1 million - $200,000 - $3,000).
2. While touring the house, you discover not only that the walls are chock-full of asbestos, but also that the ghost of Henry VII haunts the master bedroom; furthermore, a family of super-intelligent rats have built a fortress in the basement. Though you originally thought you had found the house of your dreams, you now consider it worthless. On the upside, because you bought an option, you are under no obligation to go through with the sale. Of course, you still lose the $3,000 price of the option.
 This example demonstrates two very important points. First, when you buy an option, you have a right but not an obligation to do something. You can always let the expiration date go by, at which point the option becomes worthless. If this happens, you lose 100% of your investment, which is the money you used to pay for the option. Second, an option is merely a contract that deals with an underlying asset. For this reason, options are called derivatives, which means an option derives its value from something else. In our example, the house is the underlying asset. Most of the time, the underlying asset is a stock or an index.
This example demonstrates two very important points. First, when you buy an option, you have a right but not an obligation to do something. You can always let the expiration date go by, at which point the option becomes worthless. If this happens, you lose 100% of your investment, which is the money you used to pay for the option. Second, an option is merely a contract that deals with an underlying asset. For this reason, options are called derivatives, which means an option derives its value from something else. In our example, the house is the underlying asset. Most of the time, the underlying asset is a stock or an index.
Calls and Puts
The two types of options are calls and puts:
A call gives the holder the right to buy an asset at a certain price within a specific period of time. Calls are similar to having a long position on a stock. Buyers of calls hope that the stock will increase substantially before the option expires.
A put gives the holder the right to sell an asset at a certain price within a specific period of time. Puts are very similar to having a short position on a stock. Buyers of puts hope that the price of the stock will fall before the option expires.
Participants in the Options Market
There are four types of participants in options markets depending on the position they take:
1. Buyers of calls
2. Sellers of calls
3. Buyers of puts
4. Sellers of puts
People who buy options are called holders and those who sell options are called writers; furthermore, buyers are said to have long positions, and sellers are said to have short positions.
Here is the important distinction between buyers and sellers:
-Call holders and put holders (buyers) are not obligated to buy or sell. They have the choice to exercise their rights if they choose.
-Call writers and put writers (sellers), however, are obligated to buy or sell. This means that a seller may be required to make good on a promise to buy or sell.
In order to better understand what the option is, an example of options on futures on the euro deal with this option
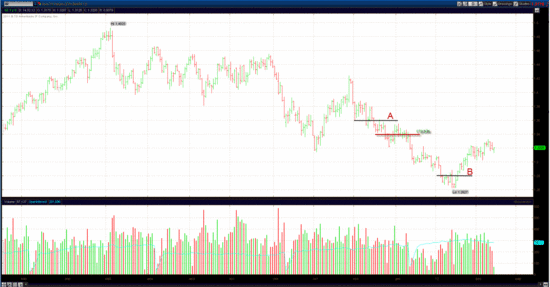
At point A, we assume that the euro will fall, and buy a put option (option which will allow us to sell the asset, futures on the euro), struck at 1.34 and lifetime 2 months (i.e., the date of expiration after 2 months). This option costs $ 750. This time, we were right, and indeed the euro fell the next 2 months. At point B we have the option to sell futures on the euro at 1.34 despite the fact that the current futures price 1.28, i.e. We fulfill our option, sell futures at price of 1.34, and we can immediately close this position, recording 600 points of profit, which translated into $ equals $7,500 profit. Subtract from this earnings premium we paid for the option and get the $ 6,750 net profit.
Thus, the use of the option allowed to increase our investment in 2 months to 10 times, or get a 1000% profit in 2 months!!!
